Mobility
The automotive industry is in a very dynamic environment and undergoing constant change. In addition to e-mobility, innovative assistance functions that enable semi-autonomous or autonomous driving are playing an increasingly crucial role. However, predicting consumption and wear is also becoming increasingly important and forms the basis for individually planned service and inspection intervals. AST's sensors play an essential role in the implementation of these technology trends. For example, our current/voltage sensors enable the measurement of currents in the range of several thousand amperes and are used in the electric drive systems of vehicles.
The H2 sensor developed by AST is an essential component of the safety design of vehicles with fuel cell-based drive systems. Furthermore, our sensors for determining service intervals and monitoring systems relevant to function and safety are increasingly finding their way into the automotive industry. Specifically, they measure and check the fill level and quality of liquids as well as the position and distances traveled in assemblies. Typical applications include, among others: systems for cleaning windshields and camera systems, battery cooling systems, and exhaust gas treatment with AdBlue®.
They are also used in brake systems, battery management systems, and a wide variety of controls in the vehicle.
High Current/High Voltage Sensors

Measuring currents in the range of thousands of amperes is a challenging task. The 3D Hall ASIC developed by AST enables the measurement of completely galvanically isolated currents without introducing additional resistance (shunts) to the path of the electric current. Even at currents above 1,000 A, the power dissipation is very low, and the temperature rise is well below that of shunt-based systems. AST's 3D Hall technology eliminates the need for ferromagnetic flux conducting elements and thus avoids the disruptive effects of hysteresis. The voltage measurement is based on an isolated high-speed digital interface and allows fast sampling rates for recording highly dynamic signals.
Battery Sensor
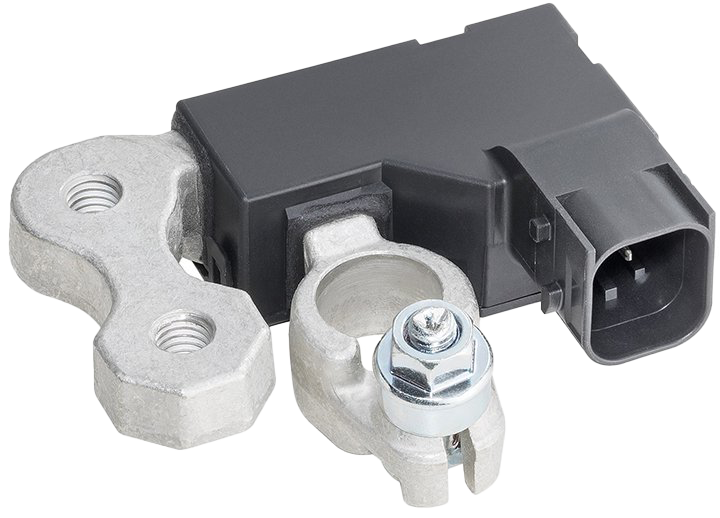
The rise of vehicle electrification is putting onboard batteries in an increasingly important role. Our high-precision battery sensors contactless determine the current, voltage, temperature, and condition of starter batteries. This allows them to provide information on the aging effects and accurately predict the remaining service life and performance.
In turn, failures due to discharged batteries and, especially in the commercial segment, cost-intensive downtimes are avoided.
Our contactless measurement method naturally has many other advantages: it is always available and also works smoothly in combination with start-stop functions and other emission-reducing measures.
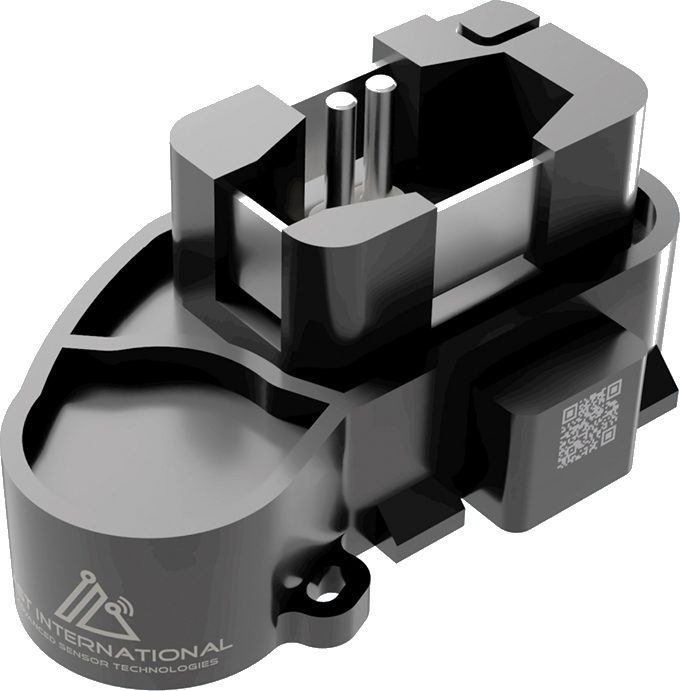
Clear Vision Sensor

Regardless of whether a vehicle is already (partially) autonomous or manually operated, driving is only possible with perfect visibility for both the driver and optical assistance systems.
Especially in poor weather conditions, this can only be ensured if there is sufficient liquid of the right quality in the cleaning system.
AST sensors continuously measure the fill level, temperature, and concentration of ethanol in the cleaning liquid (cleaning effect/antifreeze). This allows the driver to refill in time and start his journey safely. Autonomous systems use our information to determine whether a smooth ride can be guaranteed via intelligent algorithms.
Battery Cooling Fluid Sensor

Monitoring the coolant used for the direct cooling of high-performance vehicle batteries is essential for the safe operation of such systems. Especially the isolation resistance of the cooling liquid is a very critical parameter, but monitoring other fluid parameters that change with aging will help determine the optimum time for maintenance. AST's BCF sensors determine not only the isolation resistance but also the relative dielectric constant. This means they can report back continuously on the condition of the coolant and pending service work for it.
AdBlue ® Sensors

In diesel vehicles, exhaust gas treatment with AdBlue® reduces nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions by up to 90 percent. Engines equipped with this technology require sufficient amounts of AdBlue® liquid in the required quality to run smoothly.
AST's sensors monitor the fill level in the AdBlue® tank so that drivers have plenty of time to refill their tanks. The sensors also measure the quality of AdBlue®, which consists of a mixture of urea (32.5%) and demineralized water.
This ensures compliance with legal requirements and prevents misuse.
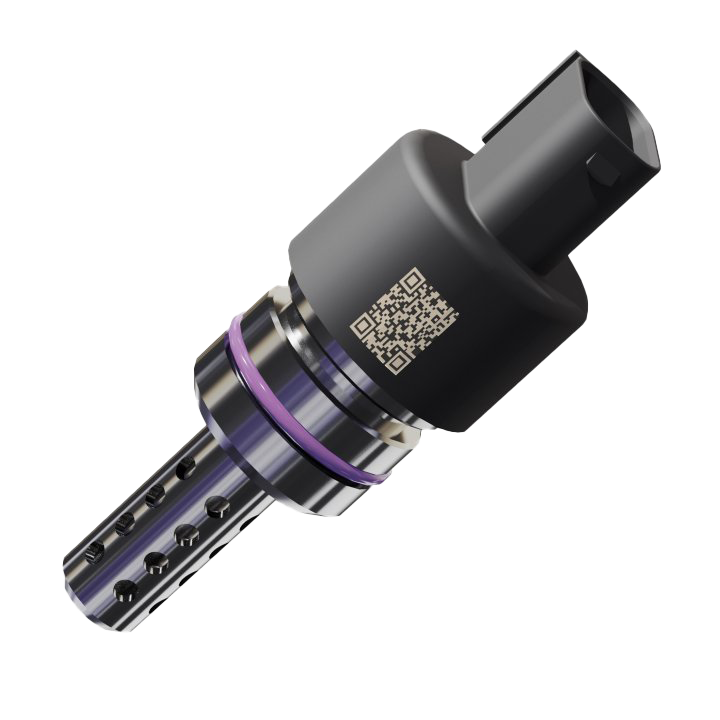
Water Injection Sensor

Water injection is a method of decreasing temperatures in internal combustion engines. It boosts performance while reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
To prevent damage to the engine, it is important to ensure that there is always sufficient demineralized water and no foreign liquids such as gasoline or windshield wiper fluid in the water tank.
AST's sensors detect foreign liquids by measuring conductivity, among other things, since distilled water is not conductive. Other non-conductive liquids can also be reliably detected.
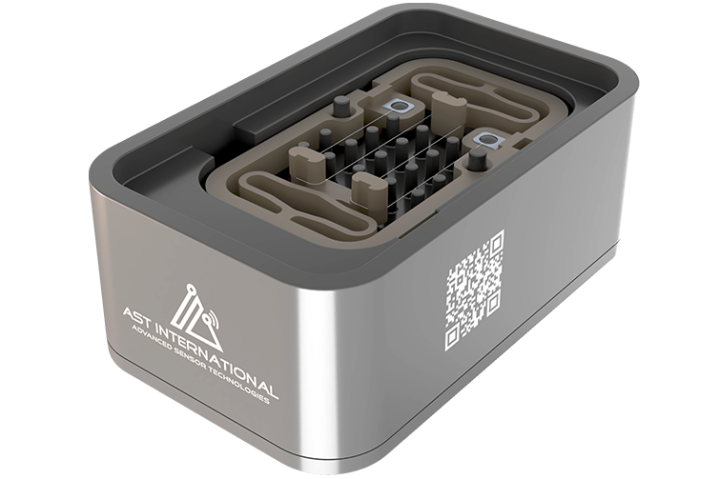
Multi-measurement Sensors
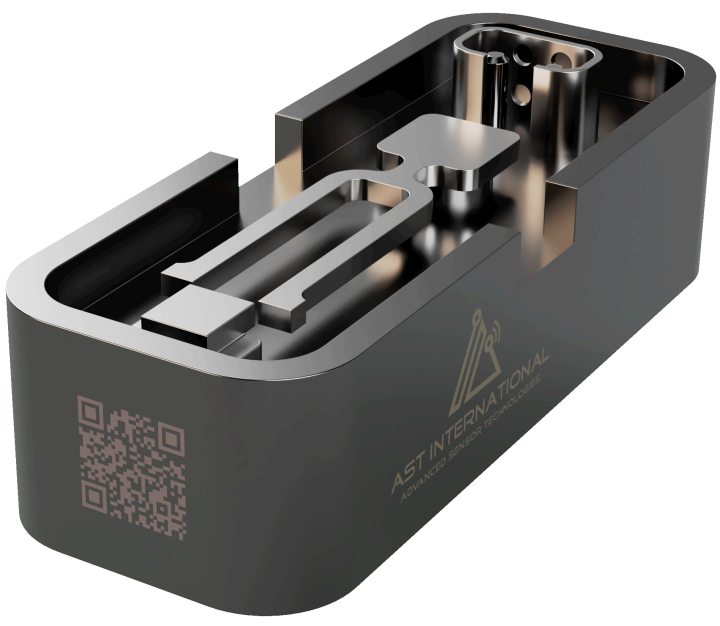

Besides preventing cost-intensive maintenance, monitoring the properties of liquids is an important task that enables the right actions to be undertaken based on the knowledge gained. The in-line detection of parameters providing information on component wear and the condition of fluids enables the optimum maintenance time to be defined and, as a safety function, the system to be shut down in the event of a detected malfunction, for example.
The AST Multi-Measurement Sensors determine a liquid's density and viscosity, isolation resistance, and relative dielectric constant. This multi-dimensional approach offers excellent performance in terms of accuracy and measurement result reliability.
Air Quality Sensor
Air quality sensors constantly monitor the intensity, degree of pollution, and number of odor molecules in the exhaust air. This information can be used as a basis for adjusting fan performance to produce a pleasantly fresh ambient climate.
By continuously measuring air pollution, our sensors intelligently predict when, for example, filters need to be replaced or the next service is due.
Wear Sensor
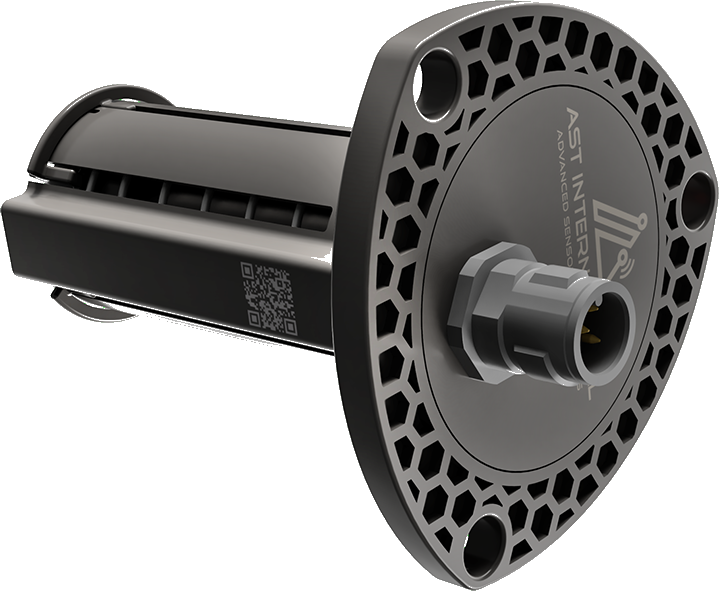

Every mechanical assembly is subject to a certain amount of wear the longer it is used. This becomes evident from, among other things, the change of a component’s shape or mechanical wear in the form of material erosion on the component’s surface. These mostly undesirable changes occur, for example, in clutches, transmissions, and brakes.
Wear impairs components’ function and effectiveness, which can lead to serious component damage and related failure. In practice, this entails the investment of additional time over and above the usual service intervals. What is merely an annoyance for the users of private vehicles leads to considerable downtime costs for commercial vehicles such as trucks or buses. After all, downtime is synonymous with lost earnings. Therefore, one tries to limit wear to easily replaceable components so-called wear parts.
Appropriate algorithms can be used to issue extremely accurate predictions about changes to the operating condition within the assembly since our intelligent sensors continuously monitor the wear on safety-relevant components and, on request, we can also determine the current temperature. This enables the individual optimization of service times. For example, our sensors in brake systems can determine whether a brake disc has been warped by thermal overload, or whether contamination is limiting the effectiveness of the brake piston, thus avoiding breakdowns and critical driving conditions.
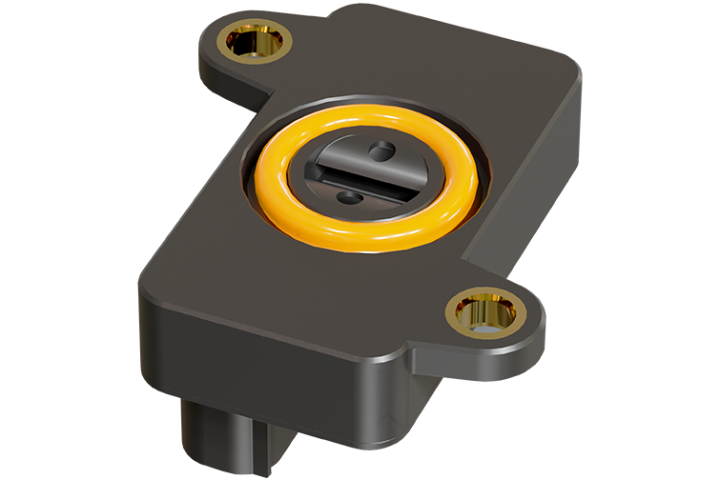
Inductive Position Sensor
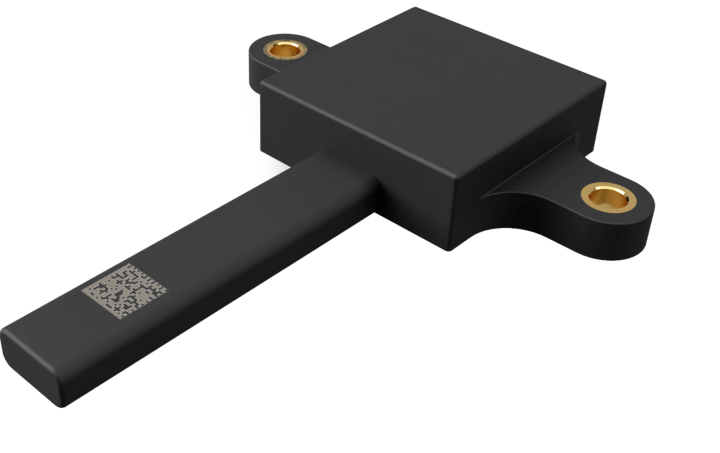
Based on the principle of inductive measurement, our position sensors determine the position of mechanical components in a contactless and wear resistant manner. The so-called target is attached to the moving part of the mechanical system and contactless interacts with the stationary sensor system via inductive mechanisms. The sensor and target are each encapsulated against environmental influences, enabling operation in harsh environments.
This enables, for example, the position of clutches, dampers, and hydraulic cylinders to be measured.
Force & Torque Sensor

Ast´s inductive force and torque sensors enable the use of structural components for measuring forces and torques. The acting forces and torques lead to minimal structural deformations, which can be precisely detected by the sensitive sensors. The measurement principle is based on eddy currents and can detect changes in shape even down to the nanometer range. The sensor electronics can be integrated into the sensor element or connected via a cable. Especially in high-temperature environments, it is recommended to keep the electronics box separate.
Pushbutton Switches
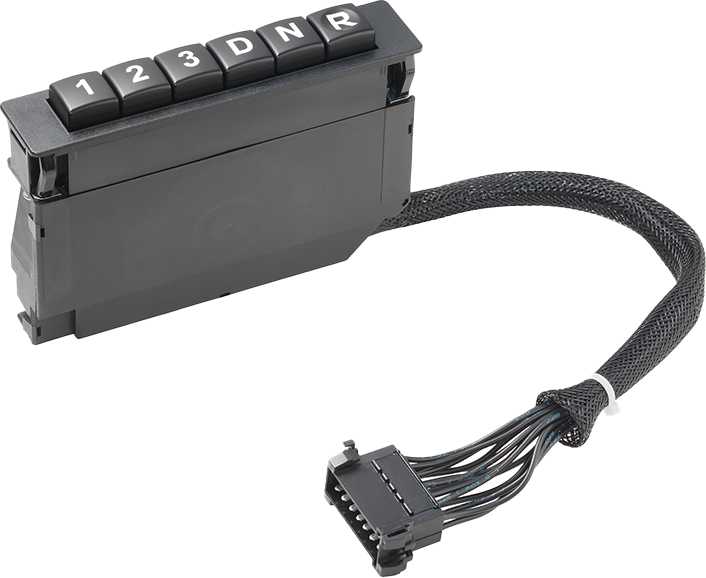

While vehicle transmissions used to be shifted purely mechanically using the gear stick via a gear linkage or cables, today the DNR switch assumes the function of the gearshift in electrically connected automatic transmissions.
Our DNR switches can be optimally positioned in vehicles so that they ergonomically adapt to the driver's seating position.
Due to their relevance to safety, the highest requirements are placed on DNR switches. Therefore, our DNR switches fulfill the requirements of the international Automotive Safety Integrity Level C (ASIL-C) standard.
Steering Column Switches

Steering column switches are controls mounted on the steering column of vehicles and are used to control an entire range of functions. Thus, they can trigger functions by tangential movement with detent or jog functions (e.g., turn signals), by pulling (e.g., headlight flasher), or pushing with and without detent (e.g., high beams). Other functions include cruise control, intermittent windshield wipers, warning lights and retarders in commercial vehicles.
Besides being resistant to wear, our sensor-based switches are designed for heavy loads and adverse environmental influences (e.g., sand, dust, and water). This makes them particularly suitable for use in commercial vehicles.
Rotary Switches
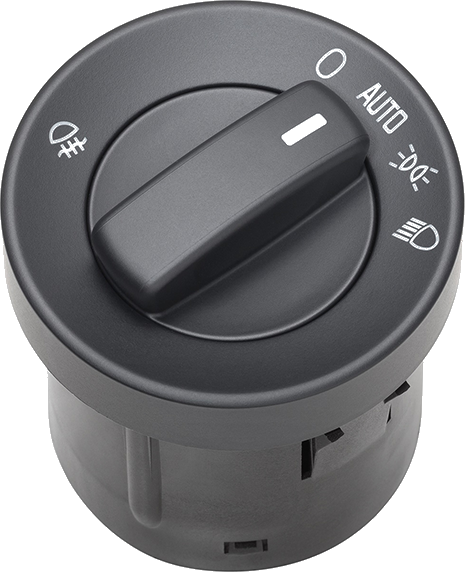

The rotary light switch is one of the classic controls in vehicles and its actuation unambiguously leads to a particular switch status.
The basic version of the three-mode switch governs the parking lights and driving lights. However, some switches are designed as rotary-pull multi-switches, which can be used to operate other light functions such as fog lights and rear fog lights, as well as the marker and position lights on commercial vehicles.
Besides being resistant to wear, our sensor-based switches are designed for heavy loads and adverse environmental influences (e.g., sand, dust, and water). This makes them particularly suitable for use in commercial vehicles.
